Array in Java
Java array is an object which contains elements of a similar
data type. Additionally, The elements of an array are stored in a contiguous
memory location. It is a data structure where we store similar elements. We can
store only a fixed set of elements in a Java array.
Array in Java is index-based, the first
element of the array is stored at the 0th index, 2nd element is stored on 1st
index and so on.
Unlike C/C++, we can get the length of
the array using the length member. In C/C++, we need to use the sizeof
operator.
In Java, array is an object of a
dynamically generated class. Java array inherits the Object class, and
implements the Serializable as well as Cloneable interfaces. We can store
primitive values or objects in an array in Java. Like C/C++, we can also create
single dimentional or multidimentional arrays in Java.
Moreover, Java provides the feature of
anonymous arrays which is not available in C/C++.
Advantages
and Disadvantage of Array and they are
Advantages
Code Optimization: It makes the code optimized, we can retrieve or sort the data efficiently.
Random access: We can get any data located at an index position.
Disadvantages
- Size Limit: We
can store only the fixed size of elements in the array. It doesn't grow
its size at runtime. To solve this problem, collection framework is used
in Java which grows automatically.
How can we declare array in java?
Here's how you can
declare an array in Java:
Datatype[] arrayname;
·
dataType can be a primitive data type like: int,
char, Double, byte etc. or an
object (will be discussed in later chapters).
Example
double [] data
But, how many elements can
array this hold?
Good
question! We haven't defined it yet. The next step is to allocate memory for
array elements.
data= new Double[10];
The length
of data array is 10. Meaning, it can hold 10 elements
(10 Double values in this case).
Note,
once the length of the array is defined, it cannot be changed in the
program.
Java Array
Index
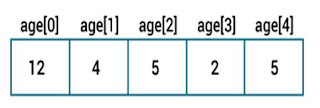
You can access elements of an array by using indices.Example
int[] age=new age[5];

array in java

The first element of array is age[0], second is age[1] and so on.
If the length of an array is n,
the last element will be arrayName[n-1]. Since the length
of age array is 5, the last
element of the array is age[4] in the above
example.
The default initial value of elements of an array is 0 for numeric types
and false for boolean.
age[0], second is age[1] and so on.arrayName[n-1]. Since the length
of age array is 5, the last
element of the array is age[4] in the above
example.false for boolean.
Example:
class ArrayExam
{
public static void main(String agrs[])
{
int[] age=new age[5];
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
System.out.println(age[i]);
}}
How to initialize arrays in Java?
In Java, you can initialize arrays
during declaration or you can initialize (or change values) later in the
program as per your requirement.
Initialize an Array During Declaration
int[] age={12,4,5,2,5};
This statement
creates an array and initializes it during declaration.
The length of the array is determined by the number of values provided
which is separated by commas. In our example, the length of
age array is 5.Simple program in java
class ArrayExam
{
public static void main(String agrs[])
{
int[] age={12,4,5,2,5};
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
System.out.println(age[i]);
}
}
}
Output:
12
4
5
3
5
Types
of Array in java
There are two types of array.
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multidimensional Array
Single Dimensional Array in Java
Syntax to Declare an Array in Java
dataType[] arr; (or)
dataType arr[];
Example
class Testarray{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]=new int[5];//declaration and instantiation
a[0]=10;//initialization
a[1]=20;
a[2]=70;
a[3]=40;
a[4]=50;
//traversing array
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++)//length is the property of array
System.out.println(a[i]);
}}
Output
10
20
70
40
50
Multidimensional Array in Java
In such case, data is stored in row and
column based index (also known as matrix form).
Syntax to Declare Multidimensional
Array in Java
dataType[][] arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType [][]arrayRefVar; (or)
dataType arrayRefVar[][]; (or)
dataType []arrayRefVar[];
Example:
//Java Program to illustrate the use of multidimensional array
class Testarray3{
public static void main(String args[]){
//declaring and initializing 2D array
int arr[][]={{1,2,3},{2,4,5},{4,4,5}};
//printing 2D array
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}}
Output:
123
245
445
Jagged Array in Java
If we are creating odd number of columns in a
2D array, it is known as a jagged array. In other words, it is an array of
arrays with different number of columns.
//Java Program to illustrate the jagged array
class TestJaggedArray{
public static void main(String[] args){
//declaring a 2D array with odd columns
int arr[][] = new int[3][];
arr[0] = new int[3];
arr[1] = new int[4];
arr[2] = new int[2];
//initializing a jagged array
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
for(int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++)
arr[i][j] = count++;
//printing the data of a jagged array
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
for (int j=0; j<arr[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();//new line
}
}
}
Output:
012
3456
78







No comments:
Post a Comment