OOPs In C++
Object means
a real word entity such as pen, chair, table etc. Object-Oriented
Programming is a methodology or paradigm to design a program using
classes and objects.
It
simplifies the software development and maintenance by providing some concepts:
- Object
- Class
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Message Passing
Object
Any
entity that has state and behavior is known as an object. For example: chair,
pen, table, keyboard, bike etc. It can be physical and logical.
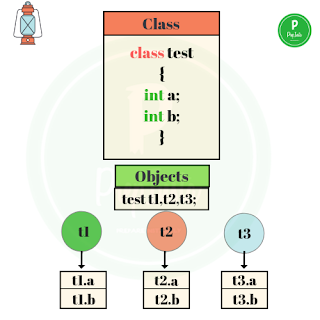
Class
Collection of objects is called class. It is a logical entity.
Inheritance
The capability of a class to derive properties and characteristics from another class is called Inheritance. Inheritance is one of the most important features of Object-Oriented Programming.
·
Sub Class: The class that inherits properties from another class is
called Sub class or Derived Class.
·
Super
Class:The class whose properties are
inherited by sub class is called Base Class or Super class.
·
Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e.
when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes
some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing
class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing
class.
Example: Dog, Cat, Cow can be Derived Class
of Animal Base Class.
Polymorphism
When one task
is performed by different ways i.e.
known as polymorphism. For example: to convince the customer differently, to
draw something e.g. shape or rectangle etc.
In C++, we use Function overloading and Function overriding to achieve polymorphism.
Abstraction
Hiding internal details
and showing functionality is
known as abstraction.
For example: phone call, we don't know the internal processing.
In
C++, we use abstract class and interface to achieve abstraction.
Encapsulation
Binding (or wrapping) code
and data together into a single unit is known as encapsulation.
For example: capsule, it is wrapped with different medicines.
Message
Passing:
Objects
communicate with one another by sending and receiving information to each
other.







No comments:
Post a Comment