Computer Fundamental Generations | Generation Of Computer Fundamental | Types Of Generation In Computer Fundamental | Computer Generation Assignment | Computer 1th To 5th | Computer generation Notes | Computer Fundamental Generation In Hindi
Computer Fundamental Generations
Computer
generations are based on major technological changes in computers
occurred, like the use of vacuum tubes, transistors, and the microprocessor. As
of 2020, there are five generations of the computer.
 |
Fig: Computer Fundamental Generation |
First generation (1940 - 1956)
The first generation of computers used vacuum
tubes as a major piece of technology. Vacuum tubes were widely used in computers from 1940 through 1956. Vacuum tubes were larger components and resulted in first
generation computers being quite large in size, taking up a lot of space in a
room. Some of the first generation computers took up an entire room.
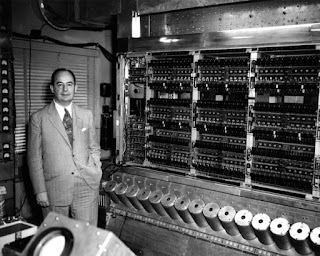 |
Fig: First Generation Image |
Second generation (1956 - 1963)
The second generation of computers saw the use of transistors instead
of vacuum tubes. Transistors were
widely used in computers from 1956 to 1963.
Transistors were smaller than vacuum tubes and allowed computers to be smaller
in size, faster in speed, and cheaper to build.
The first computer to use transistors was the TX-0 and
was introduced in 1956. Other computers that used transistors include the IBM
7070, Philco Transac S-1000, and RCA 501.
 |
Fig: Second Generation Image |
Third generation (1964 - 1971)
The third generation of computers introduced the use of IC (integrated
circuits) in computers. Using IC's in
computers helped reduce the size of computers even more compared to
second-generation computers, and make them faster.
 |
Fig: Third Generation Image |
Fourth
generation (1972 - 2010)
The fourth generation of computers took advantage of the invention of the microprocessor, more
commonly known as a CPU.
Microprocessors, along with integrated circuits, helped make it possible for
computers to fit easily on a desk and for the introduction of the laptop.
Some of the earliest computers to use a microprocessor
include the Altair 8800, IBM 5100, and Micral. Today's computers still use a
microprocessor, despite the fourth generation being considered to have ended
in 2010.
 |
Fig: Fourth Generation Image |
Fifth generation (2010 to present)
The fifth generation of computers is beginning to use AI (artificial
intelligence), an exciting technology
that has many potential applications around the world. Leaps have been made in
AI technology and computers, but there is still room for much improvement.
















